Know More About Stigma
What is Stigma?
Stigma is a discrimination against an identifiable group of people, a place, or a nation. Stigma about people with SUD might include inaccurate or unfounded thoughts like they are dangerous, incapable of managing treatment, or at fault for their condition.1
Understanding the Impact of Stigma on Addiction
Undoing Stigma
Stigma is a social process linked to power and control, which leads to creating stereotypes and assigning labels to those that are considered to deviate from the norm or to behave “badly.” Stigma creates the social conditions that make people who use drugs believe they are not deserving of being treated with dignity and respect, perpetuating feelings of fear and isolation.2
What Does Liberation Look Like?
- Liberation is the act of setting someone free from imprisonment, slavery, or oppression2
- In the context of drug use, liberation is about freedom from thoughts or behavior – “the way it’s supposed to be” — and how we are conditioned to perpetuate harms to others2
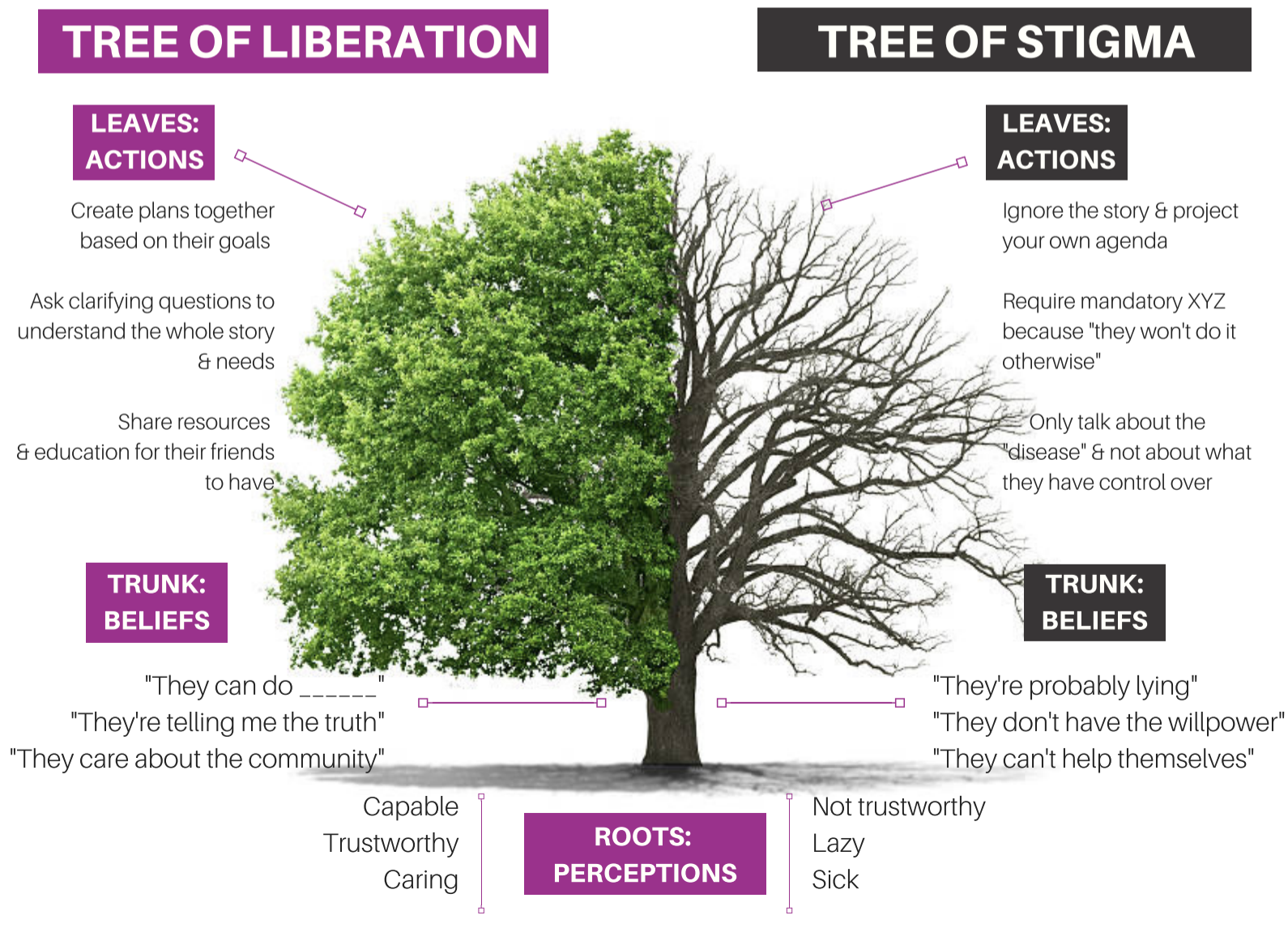
What Does Stigma Look Like?
- Stigma limits a person’s ability to access services they need because they feel unworthy of receiving or requesting services2
- Stigma creates barriers while receiving services by people feeling unwelcome or judged by program staff that offers services2
Words Matter: Terms to Use and Avoid When Talking About Addiction
 This handout offers background information and tips for providers to keep in mind while using person-first language, as well as terms to avoid for reducing stigma and negative bias when discussing addiction. Although some language that may be considered stigmatizing is commonly used within social communities of people who struggle with substance use disorder (SUD), clinicians can show leadership in how language can destigmatize the disease of addiction.3
This handout offers background information and tips for providers to keep in mind while using person-first language, as well as terms to avoid for reducing stigma and negative bias when discussing addiction. Although some language that may be considered stigmatizing is commonly used within social communities of people who struggle with substance use disorder (SUD), clinicians can show leadership in how language can destigmatize the disease of addiction.3


